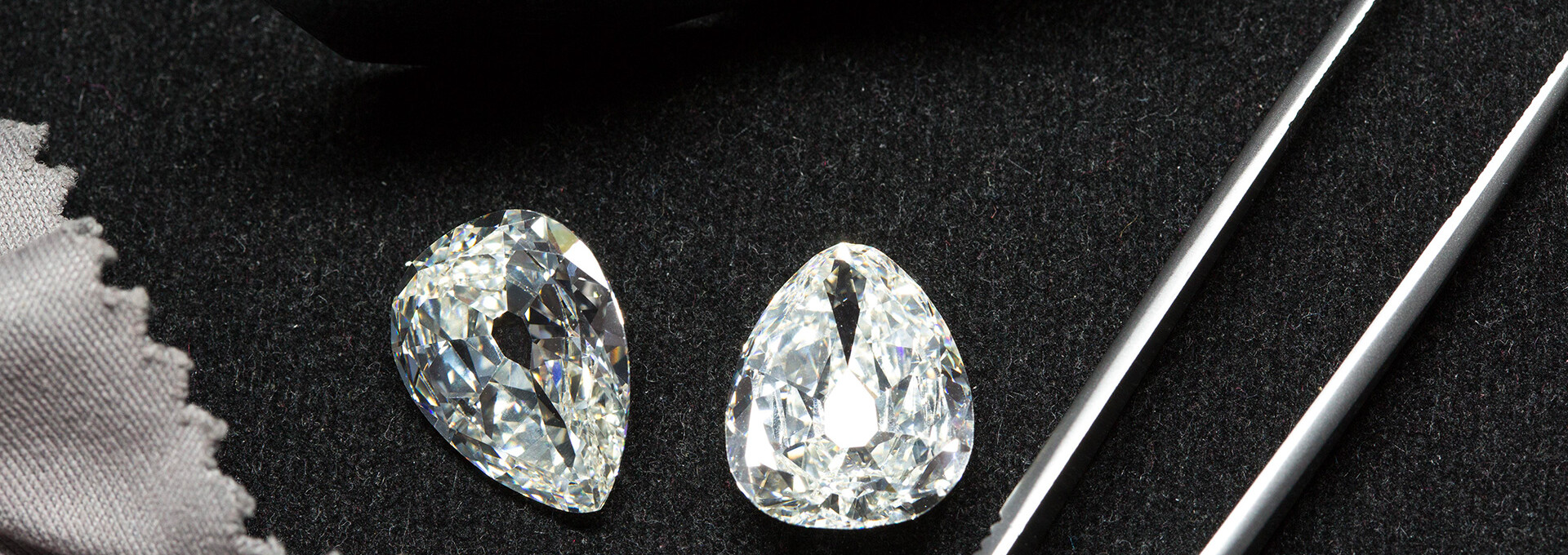
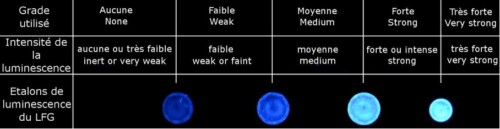
The research and identification of the treatment will be carried out for all the stones using all the state-of-the-art equipment and expertise of the Laboratoire Français de Gemmologie.
Our nomenclature is based on the recommendations of recognised international bodies such as the LMHC and the CIBJO, as well as on Decree No. 2002-65 of 14 January 2002, which governs the trade in gemstones and pearls in France.
A diamond showing no treatment will be identified as ‘Diamond’ and the information ‘No indication of treatment’ will be noted on the report.
If a diamond has one of the treatments listed below, it will be identified as a ‘Treated Diamond’ and the nature of the treatment will be noted on the report.
Nomenclature of diamond treatments :
- G - Graphitisation
- R - Irradiation
- R+TE - Irradiation followed by heat treatment
- HPHT - High pressure, high temperature
- LD - Laser drilling
- F(M) - Filling with glass enriched with heavy metals
- CG - Coating
For all these treatments, except laser drilling, LFG will not gradate the stone.